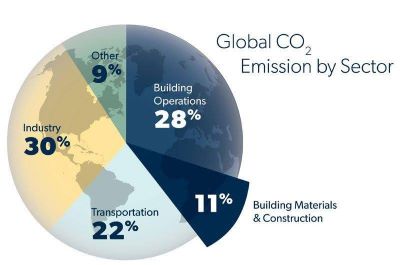
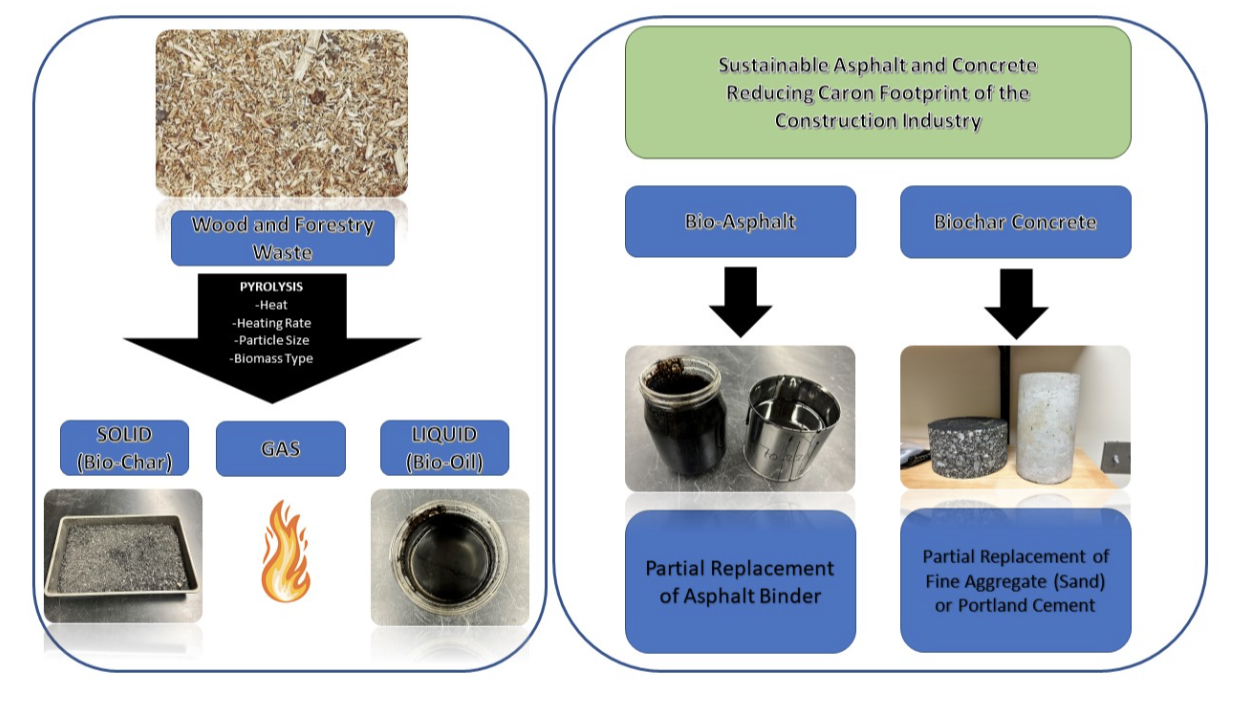
 In 2021, an ambitious target was set to reduce net greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 50-52% by 2030, and reaching global net-zero GHG emissions by 2050 or soon after. Construction industry, which is a contributor to the total GHG emissions, has also set a target of reaching net zero GHG emissions by the same year. Emissions related to construction materials can be reduced through adapting three principals: (i) reusing and recycling materials; (ii) reducing the use of virgin materials, materials optimization, and the use of low to zero carbon materials; and (iii) the use of carbon sequestering materials. On the other hand, every year a huge amount of wood and forestry waste is produced which needs to be landfilled. The use of wood waste in construction industry encourages the reduction of carbon emissions of concrete and asphalt construction, thus promoting sustainability. Using the pyrolysis process, wood and forestry waste is turned into bio-oil and biochar. The research on sustainable construction materials at the Department of Sustainable Technology and the Built Environment examines the potential of using bio-oil and biochar for partial replacement of petroleum-based asphalt binder and Portland cement, respectively.
In 2021, an ambitious target was set to reduce net greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 50-52% by 2030, and reaching global net-zero GHG emissions by 2050 or soon after. Construction industry, which is a contributor to the total GHG emissions, has also set a target of reaching net zero GHG emissions by the same year. Emissions related to construction materials can be reduced through adapting three principals: (i) reusing and recycling materials; (ii) reducing the use of virgin materials, materials optimization, and the use of low to zero carbon materials; and (iii) the use of carbon sequestering materials. On the other hand, every year a huge amount of wood and forestry waste is produced which needs to be landfilled. The use of wood waste in construction industry encourages the reduction of carbon emissions of concrete and asphalt construction, thus promoting sustainability. Using the pyrolysis process, wood and forestry waste is turned into bio-oil and biochar. The research on sustainable construction materials at the Department of Sustainable Technology and the Built Environment examines the potential of using bio-oil and biochar for partial replacement of petroleum-based asphalt binder and Portland cement, respectively.
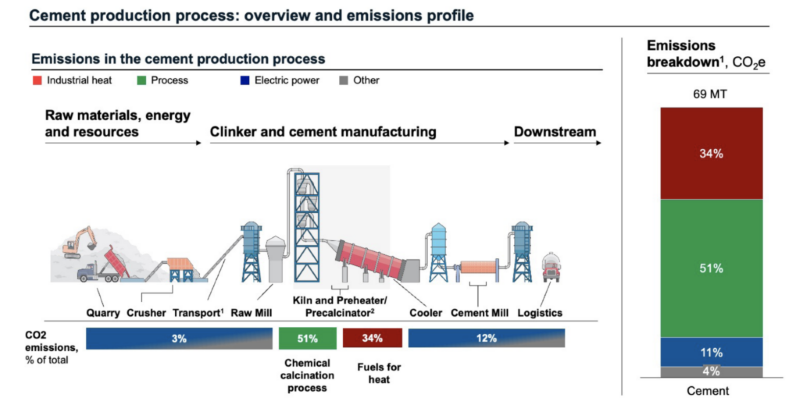
Additionally, a vast amount of waste is generated annually, much of which ends up in landfills. Incorporating waste into construction processes can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of concrete and asphalt construction, thereby promoting sustainability. Through pyrolysis, waste can be transformed into bio-oil and biochar. At the Department of Sustainable Technology and the Built Environment, research on sustainable construction materials explores the potential of using bio-oil and biochar as partial replacements for petroleum-based asphalt binders and Portland cement, respectively.
Contact
Sharareh Shirzad
shirzads@appstate.edu
Projects
- Modification of Asphalt Binder Using Wood-Based Bio-oil; Bio-Asphalt
- Polyurethane Modification of Bio-Asphalt
- Green Concrete
People
Hyla Zouzias
Publications
- Shirzad, S., Idris, I.I., Hassan, M. M., and Mohammad, L. N. (2022). "Self-Healing Capability and Mechanical Properties of Asphalt Mixtures Prepared with Light-Activated Polyurethane Prepolymer Modified Asphalt Binder." Transportation Research Record Journal of the Transportation Research Board.
- Shirzad, S., Hassan, M. M., Aguirre, M. A., Cooper, S., Mohammad, L. N., & Negulescu, I. I. (2019). "Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binder Modified with Recycled Asphalt Materials (RAS/RAP) and Light-Activated Self-Healing Polymers." Construction and Building Materials, 220 187-195.
- Shirzad, S., Hassan, M. M., Aguirre, M. A., Cooper, S., Mohammad, L. N., & Negulescu, I. I. (2019). "Mechanical Performance of Asphalt Mixtures Containing Recycled Asphalt Materials (RAP/RAS) and Light-Activated Self-Healing Polymer." Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, Vol. 31, Issue 11.